Cyber Security: What it Means and How to Attain it
Thursday 7 June 2018
Article by Jasmine Chen
Every second, 122 records are lost due to cyber-attacks. However, many of these breaches can often go unnoticed for months, and unreported for years. Why is cyber security so important? How will data breaches affect your business as well as personal life?
Dangers for Companies
The implications of data breaches are far-reaching, especially companies’ loss of reputation and revenue. After Uber’s breach incident where the personal information of 57 million Uber users and 600,000 drivers was exposed, the company saw a drop in its value from $68 billion to $48 billion, and paid the hackers millions to destroy the data (but without any ways of verifying that they did). Similarly, after Sony’s PlayStation Network accounts were hacked, the company lost $171 million loss in revenue while the site was down, and over $15 million in lawsuit settlement payment.
As technology infiltrates every part of our lives, the virtual world is slowly merging with the physical. Stuxnet, a malicious computer worm in 2010, proved that cyber-attacks can lead to physical damage. It was responsible for causing substantial damage to Iran’s nuclear program by targeting the programmable logic controllers that are used to control centrifuges separating nuclear materials. It reportedly ruined one fifth of Iran’s nuclear centrifuges and physically degraded 1000 machines after infecting over 200,000 computers.
To the dismay of many internet users, breaches may take years to be discovered, and some companies may take up to a year, if at all, to disclose the data breaches. The U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) lost up to 22 million records of highly sensitive information in background checks for current and former federal employees’ security clearances. The hacking device was installed in early 2012, but managed to remain undetected until March 20, 2014. During the investigation process, another hacker group gained access to OPM through third-party contractor in May 2014 and was not discovered until a year later.
Internet domain company Verisign suffered from a series of data theft in 2010, yet the company failed to disclose much information in regards to the exact information affected. In fact, the breaches were only disclosed due to a new SEC rules mandating its reporting. The company controls two of the internet’s thirteen root DNS servers and issues SSL digital certificates to ensure secure connections to websites. If the system is compromised, criminals can use false certificates and masquerade as websites to steal valuable personal information. Despite its far-reaching impact, Verisign refused to release additional information as the company is worried that it “could be exposed to liability and our reputation and business could suffer.”
Common Information Breached & Methods Used
Surprisingly, the healthcare industry is one of the most targeted sectors for data breaches, accounting for up to 25% of all breaches incidents. This is closely followed by financial industry with 14% of incidents. The chart below illustrates the number of incidents by industry.
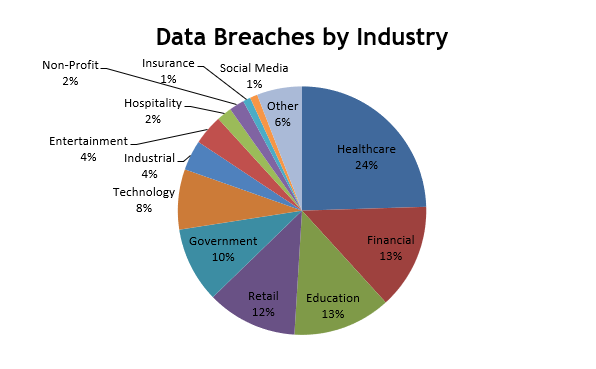
Some of the most common techniques include, stolen employee login details, SQL code injection, as well as malware and phishing. SQL injection is often used to attack data-driven applications by exploiting security vulnerability in an application’s software. It allows attackers to create fake identities, tamper with data, cause issues by avoiding transactions or changing balances, and become the administrators of the database server. It was responsible for the Heartland Payment Systems’ 2008 incident, where 134 million credit card details were exposed through SQL injection spyware. Whilst SQL injection is well understood, the continuing vulnerability of many web-facing applications made SQL injection the most common form of attack against websites.
Quick Facts
- 51% of US adults were a target of security incidents in 2016
- 65% of top 100 US banks failed the web security testing
- Worldwide, a company is hit with ransomware every 40 seconds. Amongst these, 71% of companies targeted by ransom attacks are affected
- 43% of cyber-attacks are aimed at small businesses
- Over 230,000 malware samples are produced everyday
- On average, it takes 197 days for data breaches to be detected
- Data breaches are estimated to cost companies $2 trillion by 2020, a 4-fold increase from 2015
By the time you have finished reading this article, more than 60,000 records have been compromised worldwide. It’s time to act.
To learn more, join our panel event with Gilbert and Tobin, “Successfully Navigating the Impact of a Cyber-Attack.” This event brings together a panel of experts who will work through a real life cyber-attack scenario, to help you to understand:
- what your obligations are under the law, and how to ensure you comply with them;
- how to manage the reputation fallout following a breach, and how to effectively communicate with both internal and external stakeholders; and
- the forensics behind a cyber-attack, including how data might be stolen, where it might go, and what you can do to stop it
For more information and to register, visit the event page on our website, or contact our Event Manager, Amanda Bagnall at [email protected]